Photon Theory of Light
Photon Theory of Light: Overview
This topic explains photons in relation to the light. It briefs on Planck's photon hypothesis, and Planck’s constant, energy and momentum of the photon. Furthermore, some examples based on photon theory of light are also included here.
Important Questions on Photon Theory of Light
If the energy of a photon is given as, , then, the wavelength of the photon is
Sun gives light at the rate of of the area perpendicular to the direction of the light. Assume . Calculate the number of protons/sec arriving at area at that part of the earth.
Which of the is n the property of photon?
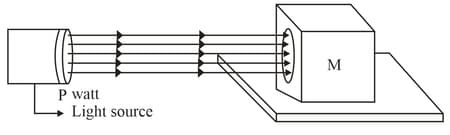
A source of light of power is shown in figure. Find the force on the block placed in the path of the light rays. The surface of body on which the light beam is incident is having a reflection coefficient = and absorption coefficient
The equation is valid
An LED is constructed from a p-n junction diode using . The energy gap is .The of light emitted will be equal to
All photons present in a light beam of a particular frequency have:
If the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron is eV. Then, the maximum stopping potential will be-____.
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
It has been experimentally demonstrated that
Minimum energy of quanta is Joule, the select the possible energy of other quanta
The energy of a photon having wavelength is:
The remote control of a TV emits infra-red light of wavelength . The TV detector is made of a semiconductor whose band gap is . The detector is shielded by a semiconductor optical filter whose band gap is . From the four options below, select the best option for the TV to function.
In a high energy experiment an electron and a positron are annihilated. The total energy of gives rise to two ray photons, each having the same energy. What will be the wavelength associated with each photon?
A laser pointer has an output power of and emits light of wavelength . What is the approximate number of photons it emits per second?
An electron in hydrogen atom makes a transition from a higher energy level to In the process a photon is emitted that has a momentum of . What is the principal quantum number of the level from where the electron made the transition?
An electron and a photon have the same wavelength. If is the momentum of the electron and is the energy of the photon, then is
In a photoelectric effect experiment, a point source of light of power emits photons each of which has energy. The source is located at a distance of from the centre of a stationary metal disk having a work function of The metal disk has a radius of Assuming that one photoelectron is emitted for every photons striking the surface of the disk, how many photoelectrons are emitted every second?
Calculate the force exerted on a small plane mirror by a plane electromagnetic wave of wave intensity which strikes the small mirror of area and the mirror is held perpendicular to the approaching wave.
Planck’s constant has the dimension of
